Share This Post
In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, businesses are constantly grappling with how best to protect their digital assets. As cyber threats grow in volume and sophistication, penetration testing has emerged as a critical tool to identify and address vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. When it comes to penetration testing, businesses often face a pivotal decision: should they opt for automated penetration testing or manual penetration testing? Each approach has advantages and limitations, and understanding which aligns with your business needs is key to building a robust cybersecurity strategy.
This blog will explore the key differences between automated and manual penetration testing, the pros and cons of each approach, and how to determine the best fit for your organization.
Outline
What is Penetration Testing?
Understanding Automated Penetration Testing
Advantages of Automated Penetration Testing
Limitations of Automated Penetration Testing
Understanding Manual Penetration Testing
Advantages of Manual Penetration Testing
Limitations of Manual Penetration Testing
Key Differences Between Automated and Manual Penetration Testing
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds
Recommended Tools for Automated Penetration Testing
Manual Penetration Testing Frameworks
FAQs
Conclusion
What is Penetration Testing?
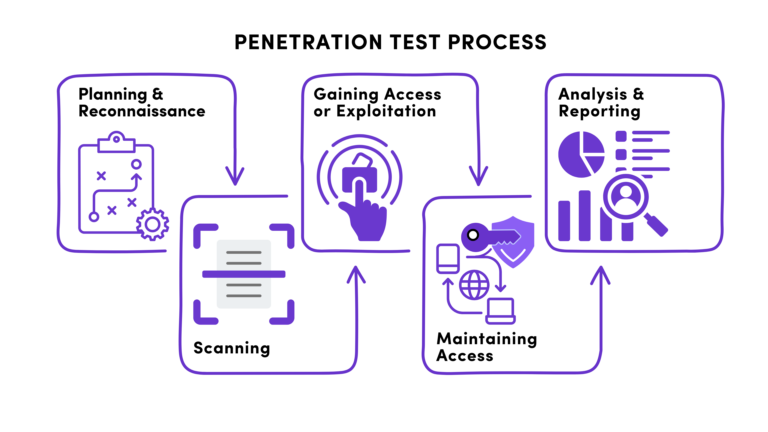
Penetration testing, often called pen testing, is a simulated cyberattack on your systems, applications, or network to uncover vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. It is an essential component of a proactive cybersecurity strategy. Businesses can take corrective measures to mitigate risks and improve their security posture by identifying weak points.
Understanding Automated Penetration Testing
Automated penetration testing involves using tools and software to scan and identify vulnerabilities in your systems. These tools use predefined scripts and algorithms to simulate attacks, providing detailed reports on discovered issues.
Advantages of Automated Penetration Testing:
- Speed and Efficiency: Automated tools can scan extensive networks and systems, making them ideal for large organizations with complex infrastructures.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Automated testing is typically more affordable than manual testing, requiring less human intervention.
- Scalability: Automated tools can handle repetitive tasks and scale quickly to test a wide range of systems simultaneously.
- Consistent Reporting: Automated tools generate standardized reports, ensuring consistency in identifying common vulnerabilities.
Limitations of Automated Penetration Testing:
- Limited Depth: Automated tools may miss complex vulnerabilities that require human intuition and creativity to uncover.
- False Positives: Automated testing can generate many false positives, requiring additional manual validation.
- Lack of Context: Automated tools cannot understand the unique context of your business, which can lead to overlooked risks.
Static Methodology: Automated tools follow predefined scripts, making adapting to dynamic and evolving threats challenging.
Understanding Manual Penetration Testing
Manual penetration testing involves skilled cybersecurity professionals simulating real-world attack scenarios to identify vulnerabilities. Unlike automated testing, manual testing relies on human expertise to uncover complex and hidden weaknesses.
Advantages of Manual Penetration Testing:
- In-Depth Analysis: Human testers can think creatively, identify sophisticated vulnerabilities, and exploit chains of vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
- Customized Approach: Manual testing can be tailored to your business context, ensuring a thorough assessment of unique risks.
- Real-World Simulation: Manual testers emulate the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of actual attackers, providing a realistic evaluation of your security.
- Fewer False Positives: Skilled testers can differentiate between genuine vulnerabilities and false positives, saving time and resources.
Limitations of Manual Penetration Testing:
- Time-Consuming: Manual testing is more time-intensive than automated tools, especially for large-scale systems.
- Higher Costs: The expertise and time required for manual testing often make it more expensive than automated testing.
Human Error: While skilled testers are highly effective, there is still potential for human error or oversight.
Key Differences Between Automated and Manual Penetration Testing
|
Feature |
Automated Testing |
Manual Testing |
|
Speed |
High |
Moderate |
|
Cost |
Low to Moderate |
High |
|
Depth |
Limited |
Comprehensive |
|
False Positives |
High |
Low |
|
Customization |
Limited |
Extensive |
|
Human Intuition |
None |
Present |
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Selecting between automated and manual penetration testing depends on several factors, including your organization’s size, budget, and security objectives. Here are some considerations to guide your decision:
1. Size and Complexity of Your IT Infrastructure
- For small businesses with simple systems, automated testing may be sufficient to identify common vulnerabilities.
- Larger organizations with complex environments may require the depth and customization of manual testing.
2. Budget Constraints
- Automated testing is a cost-effective option for businesses with limited budgets.
- However, critical systems and sensitive data may justify the higher cost of manual testing.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Specific industries, such as finance and healthcare, may have strict compliance requirements requiring manual testing to ensure thorough risk assessment.
4. Frequency of Testing
- Automated testing is ideal for frequent scans to maintain baseline security.
- Manual testing can be reserved for annual or biannual assessments or during significant system changes.
5. Type of Threats Your Business Faces
- Automated tools are effective for identifying well-known vulnerabilities.
- Manual testing is better suited to uncovering sophisticated and targeted threats.
Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds
Many businesses value adopting a hybrid approach that combines automated and manual penetration testing. This strategy leverages the speed and scalability of computerized tools alongside the depth and expertise of manual testing. For instance:
- automated penetration testing is used for regular scans and to identify low-hanging fruit.
- Complement automated testing with manual assessments to uncover more profound, complex vulnerabilities.
By integrating both methods, businesses can achieve a comprehensive and cost-effective penetration testing strategy.
Recommended Tools for Automated Penetration Testing
Some popular tools for automated penetration testing include:
- Nessus – Known for its extensive vulnerability scanning capabilities.
- Burp Suite – Ideal for web application security testing.
- OpenVAS – An open-source tool for scanning networks and systems.
- Qualys – A cloud-based platform offering automated vulnerability management.
Manual Penetration Testing Frameworks
For manual penetration testing, professionals often rely on frameworks such as:
- Metasploit – A widely-used framework for developing and executing exploit codes.
- OWASP Testing Guide – A comprehensive guide for assessing web application security.
- Cobalt Strike – A platform for adversary simulation and red team operations.
FAQs
- What is the primary difference between automated and manual penetration testing?
Automated penetration testing relies on tools and software to identify vulnerabilities quickly, while manual testing involves human expertise to uncover complex and context-specific weaknesses.
- Is automated penetration testing enough for small businesses?
For small businesses with simple IT systems, automated testing may suffice. However, periodic manual testing can provide additional assurance.
- How often should penetration testing be conducted?
Penetration testing should be conducted at least annually or after significant changes to your systems. Automated scans can be performed more frequently.
- Are there any risks associated with penetration testing?
Penetration testing, if not performed correctly, can cause system disruptions. Always work with certified professionals to minimize risks.
- Can manual and automated penetration testing be combined?
A hybrid approach combining both methods offers the best coverage, balancing efficiency and depth.
Conclusion
Both automated and manual penetration testing play crucial roles in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in your organization’s cybersecurity defenses. While automated testing offers speed, scalability, and cost-efficiency, manual testing provides depth, creativity, and real-world simulation. By understanding your business’s unique needs and leveraging a hybrid approach, you can build a robust security posture that protects your digital assets effectively.
At Axipro, we specialize in helping businesses navigate the complexities of cybersecurity. Whether you need automated testing, manual assessments, or a hybrid solution, our team of experts guides you every step of the way.