What Is DORA?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is a regulatory framework enacted by the European Union (EU) to strengthen the operational resilience of financial institutions. This act ensures businesses are equipped to manage ICT (Information and Communication Technology) risks and respond effectively to disruptions and cyber threats.
DORA applies to a diverse range of entities within the financial ecosystem. These include financial institutions like banks, insurance companies, pension funds, and investment firms; financial market infrastructures such as stock exchanges and clearing houses; critical third-party service providers, including cloud providers and IT services; and fintech companies like cryptocurrency exchanges and lending platforms. Additionally, it covers outsourcing providers, asset management firms, e-commerce platforms, and suppliers of financial products. All these entities must comply with DORA’s stringent cybersecurity, operational resilience, and third-party risk management standards to safeguard against digital disruptions.
Five Pillars of Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
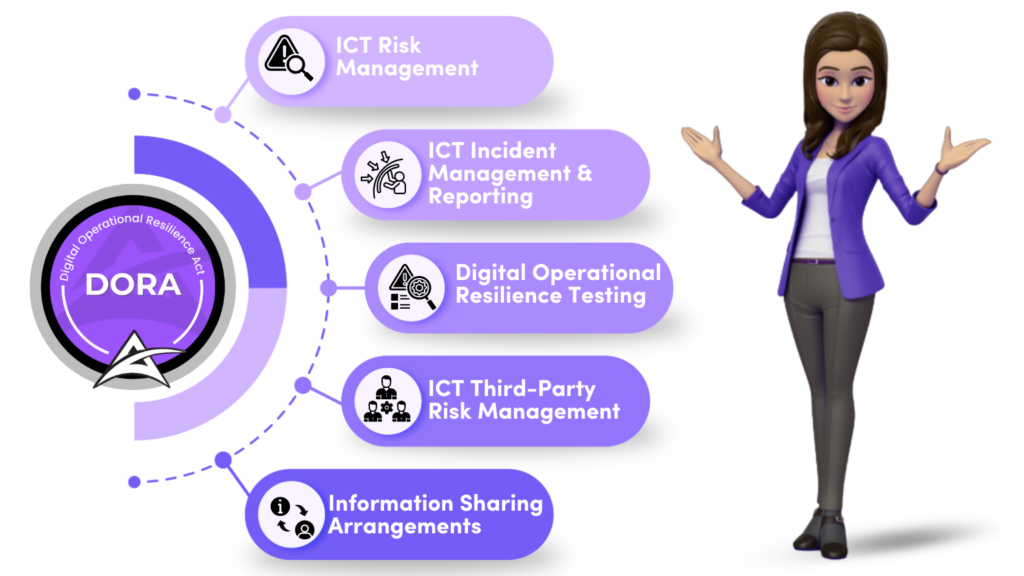

Focus of Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) focuses on enhancing the operational resilience of the financial sector by ensuring that financial institutions and their critical third-party providers are equipped to withstand, respond to, and recover from ICT-related disruptions. The regulation emphasizes robust ICT risk management, incident reporting, third-party risk oversight, and resilience testing. DORA aims to safeguard the financial system by establishing unified standards for managing digital risks and ensuring that financial entities can continue their operations even in the face of technological disruptions.
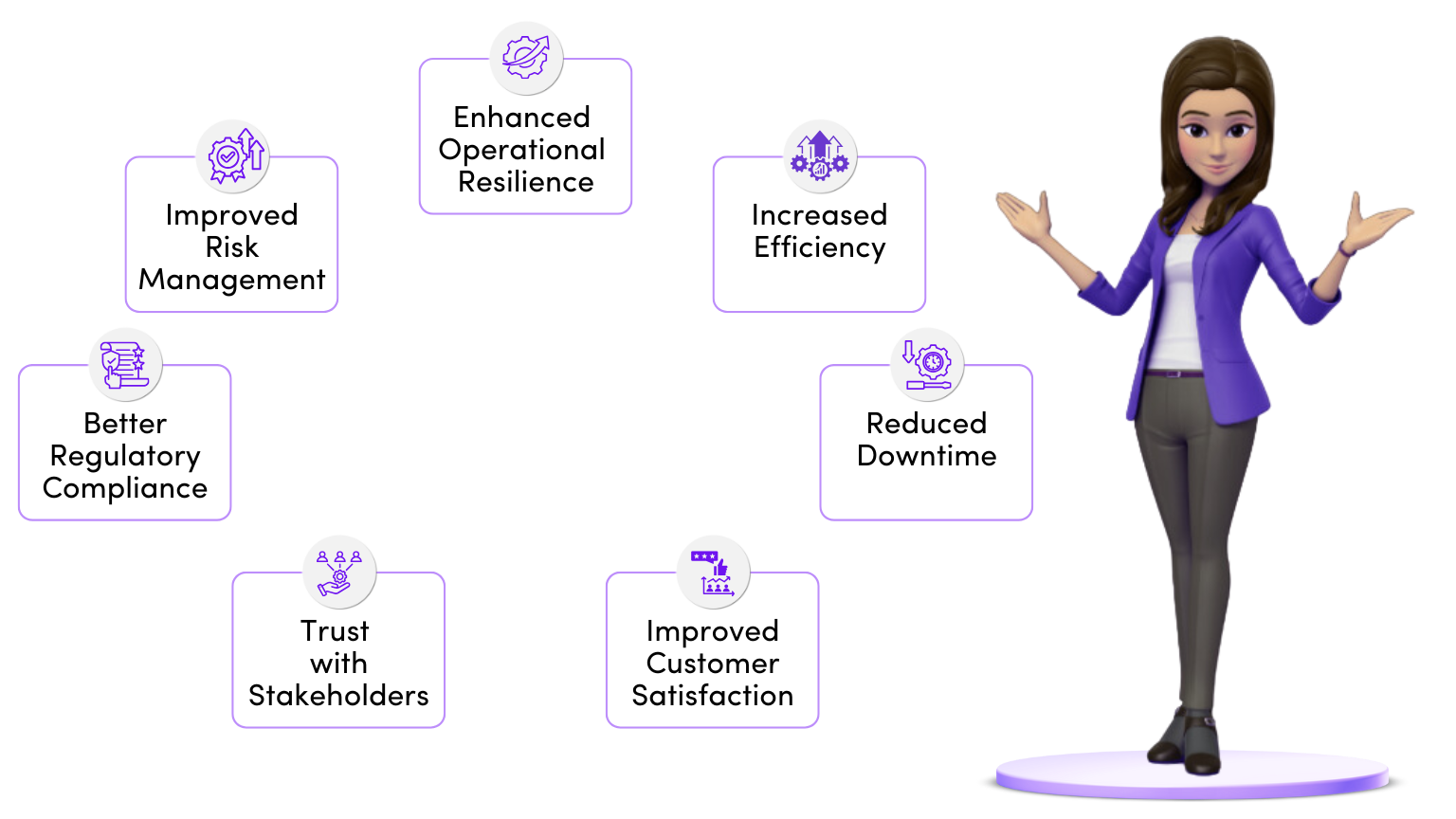
Benefits of Digital Operational Resilience Act

Risk Management
Strengthens the management of ICT risks across financial institutions, ensuring they are better equipped to handle digital disruptions.
Incident Response
Timely reporting and standardized procedures for handling ICT incidents. DORA helps organizations respond more effectively, minimizing potential losses.
Third-Party Risk Mitigation
Helps organizations safeguard their supply chain from operational disruptions by managing risks associated with third-party providers, like cloud services.
Operational Resilience Testing
DORA mandates that organizations continuously assess their ability to recover from ICT-related disruptions and enhance their crisis management strategies.
Regulatory Alignment
By aligning the with robust, EU-wide standards, DORA ensures compliance with cybersecurity norms and improves trust in the sector’s operational stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
DORA applies to a wide range of entities, including:
- Financial institutions (e.g., banks, insurance companies, pension funds).
- Financial market infrastructures (e.g., stock exchanges, clearing houses).
- Critical third-party service providers (e.g., cloud providers, data centers).
- Fintech companies (e.g., cryptocurrency exchanges, lending platforms).
- Outsourcing providers (e.g., IT services, business process outsourcing).
The primary goals of DORA are to:
- Ensure resilience against ICT disruptions.
- Improve third-party risk management, particularly with critical service providers.
- Establish common standards for ICT incident reporting.
- Require regular operational resilience testing.
- Strengthen cooperation across EU member states on cybersecurity and operational resilience.
Some of the key requirements include:
- Implementing ICT risk management frameworks.
- Reporting ICT-related incidents within strict timelines.
- Developing contingency and recovery plans for operational disruptions.
- Ensuring third-party risk management for critical service providers.
- Regular testing of operational resilience.
DORA mandates stricter controls over third-party service providers that support financial institutions. It requires financial organizations to assess and manage risks posed by critical third parties (such as cloud providers) and ensure they adhere to DORA’s operational resilience standards.
DORA requires financial institutions to report ICT-related incidents that impact their operations or the wider financial ecosystem. Incident reports must be submitted to regulators within specific timelines (typically 4 hours for major incidents), helping ensure transparency and quicker resolution.
DORA aligns with existing cybersecurity regulations, such as the EU Cybersecurity Act, by enforcing stronger governance over ICT systems. It mandates enhanced security practices, testing, and resilience measures to prevent and mitigate the impact of cyberattacks or technological disruptions on financial services.
The regulation became applicable in 2022, with organizations expected to comply by 2024. Financial entities and their third-party providers must demonstrate compliance by developing and implementing comprehensive ICT risk management and resilience frameworks.
DORA applies to various fintech companies, including cryptocurrency exchanges and digital payment platforms. These entities must adhere to the same resilience, incident reporting, and third-party risk management requirements, ensuring their services remain operational despite digital disruptions.
Penalties for non-compliance with DORA can include significant fines and reputational damage. The regulation emphasizes the importance of timely and thorough compliance with its requirements, particularly regarding incident reporting and operational resilience.


